Within the Horizon2020 Treasure project, the Scuola universitaria professionale della Svizzera italiana (SUPSI)’s SPS lab has developed a sustainability and circularity Assessment and Advisory methodology.
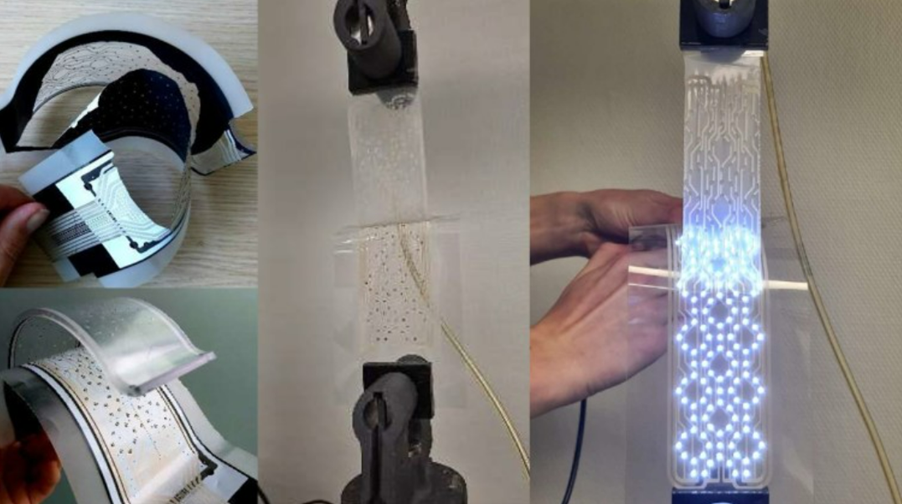
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are state-of-the-art when it comes to creating electronic functions, but pose challenges with respect to sustainability. These highly integrated electronic products, where plastics, metals and semiconductor components are seamlessly combined, are a challenge to recycle. The only suitable end-of-life scenario is still limited to shredding and incineration.
There is a more eco-friendly alternative to PCBs: Hybrid and Printed Electronics (HPE). This technology is a big step forward compared to PCBs, but much more is needed to achieve circular production of next-generation electronics.
This methodology, encompassing environmental, economic, social, and circularity aspects, incorporates key indicators and calculation methods to offer structured guidance to decision-makers.
Designed to empower automotive dismantlers, recyclers, and designers in making informed decisions that enhance sustainability performance, our methodology is now undergoing validation in collaboration with TNO, Walter Pack and SEAT, S.A. We are applying it to the TREASURE eco-design use case, specifically comparing IMSE technology with the traditional PCB production process to determine the most sustainable and circular solution.
More information on the work of TNO on sustainable IMSE is available in the following article: https://lnkd.in/dyurrFhV